


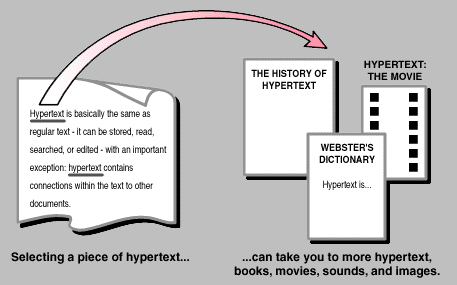
The World-Wide Web is officially described as a "wide-area hypermedia information retrieval initiative aiming to give universal access to a large universe of documents". What the World-Wide Web (WWW, W3) project has done is provide users on computer networks with a consistent means to access a variety of media in a simplified fashion.

European Laboratory for Particle Physics in Geneva, Switzerland
Integration of earlier Internet systems
Platform independent
Format independent
Multiple Media
A Little History
1989
Tim Berners-Lee and Robert Cailliau propose a networked Hypertext project for High-Energy Physics collaborations
1990
The system is available on the NeXTStep operating system
Further proposal for a Hypertext project for CERN
The name World-Wide Web is decided
1991
The universally portable LMB (Line-Mode Browser) is distributed
Work starts on a Macintosh version
We demonstrate at the San Antonio Hypertext Conference
An X-Window browser is urgent.
1992
people at SLAC, FNAL, NIKHEF, DESY join with servers
1993
NCSA releases X-Mosaic, colour images arrive!
Work starts on a PC version
NCSA releases Mac and PC versions of Mosaic
WWW becomes the Internet demo
1994
CommerceNet started
First International Conference
Overtake Gopher traffic
European Commission project
NetScape "buys up" all manpower
Total shock wave
Driving the Internet expansion
Second International Conference
Tim leaves for MIT
1995
European development is transferred from CERN to INRIA
WWW/Internet fuse in the minds of non-specialists
WWW at the basis of the special G7 conference in Brussels
Third International Conference
First regional conference
Fourth International Conference








|

|
|
GIF Compuserve's Graphic Interchange Format Very common compression scheme |
JPEG Tighter compression - smaller files Not as many browsers support JPEG images |





set HOTJAVA_DSIABLE_SOUND=true
Virtual Reality Modeling Language (VRML) - Everything you want to know about it and more!
VRML at NCSA
Sample VRML Sites
SGML - Standard Generalized Markup Language
DTD - Document Type Definition - a specific markup language written using SGML
HTML - HyperText Markup Language, a SGML DTD
SGML browser Panorama is availalbe for Windows and is working together with NCSA Mosaic
SGML
More on SGML can be found at A Gentle Introduction to SGML




